Self-learning Data Systems
Database systems are becoming increasingly complex. Manually configuring a system for each different system environment is too time-consuming and, more than often, not even optimal. To build self-optimizing systems, I am investigating machine learning-based techniques that can continuously optimize the internals of data systems.
Database systems are becoming increasingly complex. Manually configuring a system for each different system environment is too time-consuming and, more than often, not even optimal. To build self-optimizing systems, I am investigating machine learning-based techniques that can continuously optimize the internals of data systems.
QuickSel
Estimating the selectivity of a query is a key step in almost any cost-based query optimizer. Most of today’s databases rely on histograms or samples that are periodically refreshed by re-scanning the data as the underlying data changes. Since frequent scans are costly, these statistics are often stale and lead to poor selectivity estimates. As an alternative to scans, query-driven histograms have been proposed, which refine the histograms based on the actual selectivities of the observed queries. Unfortunately, these approaches are either too costly to use in practice—i.e., require an exponential number of buckets—or quickly lose their advantage as they observe more queries. In this paper, we propose a selectivity learning framework, called QuickSel, which falls into the query-driven paradigm but does not use histograms. Instead, it builds an internal model of the underlying data, which can be refined significantly faster (e.g., only 1.9 milliseconds for 300 queries).
Database Learning

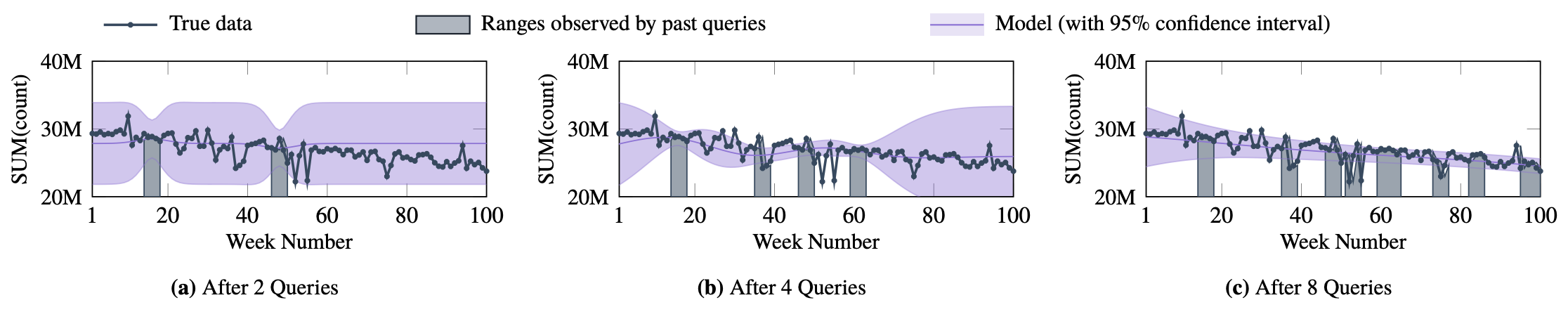
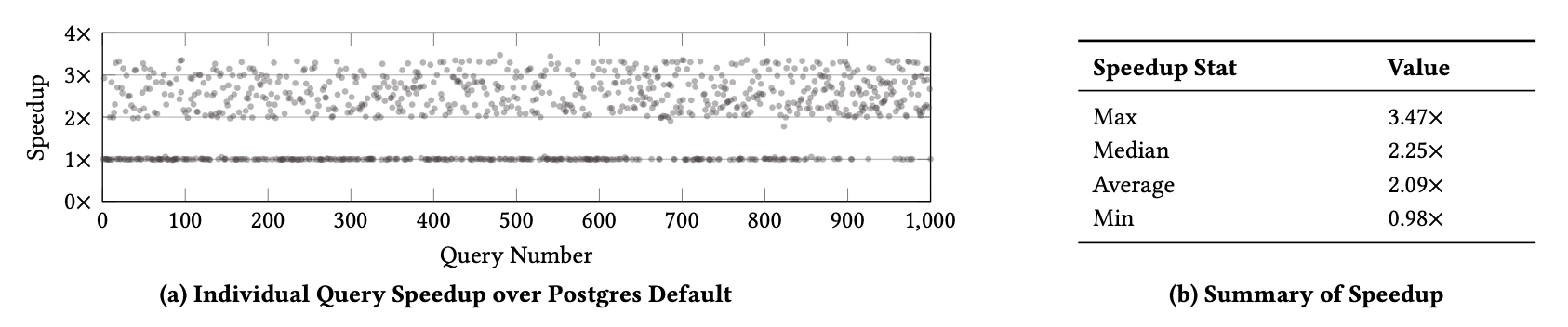
In today’s databases, previous query answers rarely benefit answering future queries. For the first time, to the best of our knowledge, we change this paradigm in an approximate query processing (AQP) context. We make the following observation: the answer to each query reveals some degree of knowledge about the answer to another query because their answers stem from the same underlying distribution that has produced the entire dataset. Exploiting and refining this knowledge should allow us to answer queries more analytically, rather than by reading enormous amounts of raw data. Also, processing more queries should continuously enhance our knowledge of the underlying distribution, and hence lead to increasingly faster response times for future queries.
We call this novel idea—learning from past query answers—Database Learning. We exploit the principle of maximum entropy to produce answers, which are in expectation guaranteed to be more accurate than existing sample-based approximations. Empowered by this idea, we build a query engine on top of Spark SQL, called Verdict. We conduct extensive experiments on real-world query traces from a large customer of a major database vendor. Our results demonstrate that database learning supports 73.7% of these queries, speeding them up by up to 23.0x for the same accuracy level compared to existing AQP systems.